What is OCR Technology? A Complete Guide to Optical Character Recognition

Accuracy, speed, and compliance are essential to efficient Identity Verification (IDV) and business processes. With digital transformation accelerating, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) has become a cornerstone technology. From banking to healthcare, OCR streamlines operations, reduces costs, and unlocks automation at scale. In this guide, we’ll break down what OCR is, how it works, and why Ondato’s AI-powered OCR is redefining compliance and verification.
What is OCR Technology?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that enables machines to automatically detect and extract text and data from physical documents, scanned images, or even an image file captured with a smartphone. Instead of relying on manual entry, OCR software can “read” printed or handwritten characters in scanned paper documents, printed paper documents, or even scanned legal documents, and transform them into structured, digital data. This data can then be stored, searched, and processed through modern databases and compliance systems.
A Brief History of OCR
The concept of OCR — sometimes referred to as optical word recognition — dates back to the early 20th century, when inventors first experimented with mechanical devices to help the visually impaired read printed text. Over time, these early machines gave way to software-driven systems and OCR programs.
Early OCR: Early versions of OCR were rigid and rule-based. They relied on simple pattern recognition, which meant they could only interpret very specific fonts and standardized layouts. If a scanned document was misaligned, of poor quality, or handwritten, these systems often failed.
AI-powered OCR: The introduction of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) completely revolutionized the field. Instead of relying solely on pattern-matching, modern OCR software leverages intelligent character recognition (ICR) and deep learning models trained on millions of text samples. This enables them to recognize diverse fonts, handwritten notes, and even poor-quality scans with much higher accuracy.
Why OCR Matters Today
OCR enables automated data extraction from scanned paper documents, invoices, contracts, and IDs, drastically reducing the need for manual data entry. This efficiency allows businesses to scale quickly, processing thousands of files per second, which is impossible with human labor.
OCR also makes information accessible by converting scanned legal documents, financial statements, or medical records into searchable and editable formats. In compliance-heavy sectors such as banking and healthcare, OCR ensures regulatory requirements are met by capturing customer and identity data with accuracy and security in mind.
Ultimately, OCR bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. Whether it’s digitally onboarding a banking client, digitizing patient records, or verifying an ID through OCR verification, this technology ensures critical information flows seamlessly into modern systems making them faster, more reliably, and with less risk.
How OCR Technology Works
At its core, OCR transforms images of text into usable digital information. While this sounds straightforward, the process involves several sophisticated steps designed to maximize accuracy and reliability.
Step 1: Scanning & Preprocessing
The journey begins with capturing the document, whether it’s an ID card, passport, invoice, or handwritten note. Once the image is obtained, the system applies preprocessing techniques to prepare it for recognition. These steps include:
- Noise Reduction: Removing visual distortions like speckles, shadows, or background patterns.
- Contrast & Brightness Adjustment: Enhancing readability by clarifying faint or overexposed text.
- Text Zone Detection: Identifying where relevant text is located (for example, distinguishing between a signature box, photo, and printed information).
- Alignment & Skew Correction: Rotating or straightening images so characters appear in their intended orientation.
This stage ensures that the OCR engine is analyzing the cleanest, most legible version of the document.
Step 2: Text Recognition
Once the image is preprocessed, the OCR engine begins the recognition phase, which is the heart of the technology. Here’s how it works:
- Character Pattern Analysis: The system examines shapes and patterns that resemble letters, numbers, or symbols.
- Machine Learning Models: Trained on millions of text samples, modern OCR engines can identify fonts, handwriting styles, and even symbols across different languages.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Context matters — NLP allows the system to predict likely words or phrases, reducing errors (for example, distinguishing “0” from “O” based on surrounding text).
This combination of pattern recognition, AI, and linguistic context ensures a much higher success rate compared to traditional rule-based systems.
Step 3: Data Extraction & Structuring
Recognition is only the beginning. The extracted characters must be converted into usable data:
- Formatting: Converting raw text into structured fields (names, addresses, dates, document numbers).
- Validation: Checking extracted information against expected formats (e.g., a passport number must fit a specific pattern).
- Integration: Delivering clean, machine-readable data into databases, compliance systems, or onboarding workflows.
This is where OCR proves most valuable — turning a static image into actionable data.
Basic OCR vs. Advanced AI OCR
Not all OCR systems are the same, and the gap between traditional and AI-powered solutions is significant.
Basic OCR works well when the conditions are ideal — clean, printed text in standardized formats. However, it struggles when faced with poor-quality scans, unusual fonts, or handwriting. Its character-by-character approach lacks contextual understanding, which means errors are more common in real-world applications.
Advanced AI-powered OCR, on the other hand, goes far beyond simple recognition. By leveraging neural networks and deep learning, it continuously improves its accuracy over time. It can process multiple languages, including non-Latin scripts, and remains effective even with low-quality images. With natural language processing (NLP), AI OCR interprets context, reducing errors like mistaking the number “0” for the letter “O.” Importantly, it can also be customized for compliance-driven workflows such as eKYC and AML, making it suitable not just for digitization but for highly regulated industries.
Key Applications of OCR Technology
OCR has become a cornerstone of digital transformation because it eliminates manual data entry and makes unstructured information usable. Its versatility means it is now applied across nearly every industry:
Document Digitization
Governments, libraries, and enterprises rely on OCR to preserve and unlock historical, machine-readable text documents or printed documents. By converting physical documents into searchable, digital files, organizations can ensure knowledge is accessible, secure, and easy to retrieve.
Financial Services & Compliance
Banks, fintechs, and KYC/AML providers use OCR to accelerate onboarding and meet regulatory obligations. Instead of manually entering passport or ID data, OCR automates extraction and verification, significantly reducing processing times and human error. Beyond identity verification, it also supports invoice scanning and automated reconciliation in accounting workflows.
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics use OCR to digitize patient records, prescriptions, lab reports, and insurance claims. This not only saves time but also improves patient safety by ensuring medical data is accurately captured and integrated into electronic health record (EHR) systems.
Retail & Logistics
From scanning receipts at checkout to reading barcodes and shipping labels, OCR helps retailers and logistics companies streamline operations. It reduces errors in order tracking, accelerates returns processing, and enables better supply chain visibility.
Legal & Insurance
Law firms and insurers deal with mountains of paperwork. OCR automates contract analysis, extracts key clauses, and processes claims documentation quickly, cutting down on review times and making compliance audits more efficient.
Benefits of OCR Technology
The rise of OCR technology is about transforming the way organizations work. By replacing manual processes with automation, OCR delivers tangible benefits across efficiency, cost, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Efficiency & Speed
OCR can process documents in seconds, a task that would otherwise take employees hours. This speed is particularly valuable in industries where time is critical, such as banking (onboarding new customers), healthcare (retrieving patient records), or logistics (processing shipping labels). Faster processing means businesses can handle larger volumes without scaling headcount.
Cost Reduction
Manual data entry is not only time-consuming but also expensive. By automating routine tasks, OCR helps organizations reduce labor costs and allocate staff to higher-value work, such as customer service or fraud prevention. Over time, these savings compound, making OCR a cost-efficient investment.
Accuracy & Error Reduction
Human error is inevitable when dealing with repetitive data entry. OCR dramatically reduces mistakes by consistently extracting and validating information against set formats. Advanced AI-powered OCR goes a step further, using context awareness to prevent common errors (e.g., confusing “1” with “I” or “0” with “O”). This reliability strengthens trust in data-driven decisions.
Improved Customer Experience
In a digital-first world, speed and simplicity define customer expectations. OCR supports seamless onboarding and verification processes, eliminating friction caused by long forms or repeated manual checks. Whether it’s opening a bank account, filing an insurance claim, or verifying identity for an online service, OCR ensures that the process is quick, accurate, and frustration-free.
OCR Technology Challenges
Despite its many advantages, OCR is not without limitations. One of the most common hurdles is the quality of the source material. Low-resolution scans, blurred photos, or documents with glare and shadows can significantly reduce recognition accuracy, making it difficult to extract reliable data. Handwriting remains another challenge. While modern AI-powered OCR can interpret certain handwritten notes, complex or stylized handwriting is still prone to misinterpretation.
Language diversity also poses difficulties. Supporting non-Latin alphabets, such as Arabic, Cyrillic, or Chinese ideograms, requires advanced machine learning models trained on vast, varied datasets. Even then, rare scripts or mixed-language documents can lower performance. Finally, because OCR often processes sensitive information like identity documents or medical records, data security and privacy are critical concerns. Systems must be designed to comply with regulations such as GDPR and other data protection laws, ensuring information is handled responsibly and securely.
The Role of OCR in Compliance and Verification
While OCR has broad applications across industries, its impact is particularly powerful in regulated sectors where compliance and identity verification are non-negotiable. Financial institutions, fintechs, insurers, and other businesses subject to strict regulations rely on OCR to make compliance processes faster, more secure, and less prone to error.
KYC & AML Checks
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations require organizations to verify the identity of customers before offering services. OCR automates this process by extracting critical data, such as names, dates of birth, ID numbers, and expiration dates, directly from passports, IDs, or driving licenses. This eliminates manual entry, reduces delays, and ensures customer data is captured accurately during onboarding.
Regulatory Compliance
Beyond onboarding, OCR plays a key role in ensuring ongoing adherence to global data protection frameworks. For example, in the European Union, OCR systems can be designed to process and transmit personal data in ways that align with GDPR requirements. Automating data collection also ensures that companies maintain consistent, audit-ready records, which is critical when facing regulatory reviews or inspections.
Fraud Prevention & Risk Reduction
OCR technology contributes to stronger fraud defenses by validating document authenticity and spotting inconsistencies that might indicate tampering. Combined with AI models and other verification tools, OCR helps organizations flag fake or altered IDs before they become a threat. This ability to quickly and accurately assess documents not only reduces financial and reputational risks but also strengthens customer trust in digital onboarding.
OCR vs. OCR Verification
It’s important to distinguish between OCR technology and OCR verification:
- OCR technology is the broad process of digitizing and extracting text from documents.
- OCR verification applies OCR within compliance workflows, ensuring extracted data is validated against regulations like AML and KYC.
OCR verification is what allows businesses to not just digitize documents but also meet legal obligations.
Ondato’s AI-Powered OCR Technology
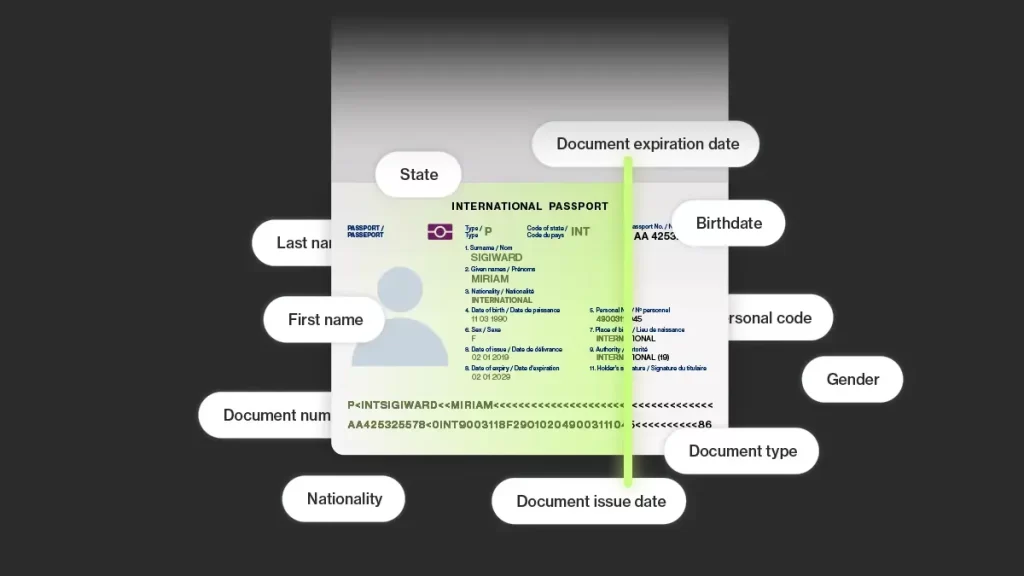
Ondato brings OCR innovation to the compliance landscape. Initially developed for its own identity verification solutions, Ondato now offers OCR as a standalone API for global businesses.
- Speed & Accuracy: Processes over 10,000 document templates in less than a second with accuracy rates up to 99.8%.
- Global Accessibility: Works across 186 countries, supporting nearly all languages, alphabets, and scripts, including Chinese ideograms and Cyrillic.
- Compliance-Ready: Data is securely processed and stored on client servers, aligned with GDPR and global standards.
- Integration Options: Available as a standalone API or part of Ondato’s IDV solutions, empowering KYC providers, financial institutions, and online platforms.
With Ondato’s AI-powered OCR, businesses achieve faster onboarding, reduced fraud risk, and a fully compliant verification process.
The Future of OCR Technology
The future of OCR is being shaped by rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Accuracy is expected to improve even further, as new models are trained to recognize complex handwriting and compensate for poor-quality scans. What once required pristine documents will soon be possible with images captured in less-than-ideal conditions, expanding OCR’s reliability in real-world scenarios.
Real-time OCR is also emerging as a powerful development. With the growth of mobile and cloud-based systems, document verification can happen instantly, no matter where the user is located. This has the potential to transform industries like banking, travel, and e-commerce, where speed and convenience are essential.
Finally, OCR is becoming more deeply integrated into compliance and risk management ecosystems. Beyond simply reading and digitizing documents, it is evolving into a tool that supports fraud detection, facilitates secure e-signatures, and strengthens end-to-end identity verification workflows. As organizations seek greater automation and stronger safeguards, OCR will continue to be a critical enabler of digital trust.